GATE 2005-IT
Question 1 |
A bag contains 10 blue marbles, 20 green marbles and 30 red marbles. A marble is drawn from the bag, its colour recorded and it is put back in the bag. This process is repeated 3 times. The probability that no two of the marbles drawn have the same colour is
1/36 | |
1/6 | |
1/4 | |
1/3 |
Total possible combinations = 3! = 6
Probability of blue marble = 10/60[10 + 20 + 30 = 60]
Probability of green marble = 20/60
Probability of red marble = 30/60
The probability that no two of the marbles has same colour = [10/60 * 20/60 * 30/60] = 1/6
Question 2 |
If the trapezoidal method is used to evaluate the integral obtained 0∫1x2dx ,then the value obtained
is always > (1/3) | |
is always < (1/3) | |
is always = (1/3) | |
may be greater or lesser than (1/3) |
Question 3 |
The determinant of the matrix given below is

-1 | |
0 | |
1 | |
2 |

determinant = product of diagonal element [upper triangular matrix]
= -1 * 1 * 1 * 1
= -1
Question 4 |
Let L be a regular language and M be a context-free language, both over the alphabet Σ. Let Lc and Mc denote the complements of L and M respectively. Which of the following statements about the language if Lc ∪ Mc is TRUE?
It is necessarily regular but not necessarily context-free. | |
It is necessarily context-free. | |
It is necessarily non-regular. | |
None of the above. |
Question 5 |
Which of the following statements is TRUE about the regular expression 01*0?
It represents a finite set of finite strings. | |
It represents an infinite set of finite strings. | |
It represents a finite set of infinite strings. | |
It represents an infinite set of infinite strings. |
So, given regular expression represents an infinite set of finite strings.
Question 6 |
The language {0n 1n 2n | 1 ≤ n ≤ 106} is
regular | |
context-free but not regular | |
context-free but its complement is not context-free | |
not context-free |
So, given language is regular.
Question 7 |
Which of the following expressions is equivalent to (A⊕B)⊕C
 | |
 | |
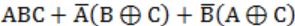 | |
None of these |
⇒ We know that
A⊕B = A'B + AB'
A⊙B = AB + A'B' ⇒ (A⊕B)'C + (A⊕B)C'
⇒ (A⊙B)C + (A'B + AB')C'
⇒ (AB + A'B')C + (A'B + AB')C'
⇒ ABC + A'B'C + A'BC' + AB'C'
⇒ ABC + (A'B'C + A'B'C) + A'BC' + AB'C'
[We know that A + A = A]
⇒ ABC + A'B'C + A'B'C + A'BC' + AB'C'
⇒ ABC + A'(B'C + BC') + B'(A'C + AC')
⇒ ABC + A'(B⊕C) + B'(A⊕C)
Question 8 |
Using Booth’s Algorithm for multiplication, the multiplier -57 will be recoded as
0 -1 0 0 1 0 0 -1 | |
1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 | |
0 -1 0 0 1 0 0 0 | |
0 1 0 0 -1 0 0 1 |
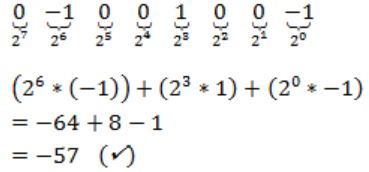
Question 9 |
A dynamic RAM has a memory cycle time of 64 nsec. It has to be refreshed 100 times per msec and each refresh takes 100 nsec. What percentage of the memory cycle time is used for refreshing?
10 | |
6.4 | |
1 | |
.64 |
In 106ns refresh 100 times.
Each refresh takes 100ns.
Memory cycle time = 64ns
Refresh time per 1ms i.e., per 106ns = 100 * 100 = 104ns
Refresh time per 1ns = (104)/(106) ns
Refresh time per cycle = (104*64)/(106) = 64ns
Percentage of the memory cycle time is used for refreshing = (64*100)/64 = 1%
Question 10 |
A two-way switch has three terminals a, b and c. In ON position (logic value 1), a is connected to b, and in OFF position, a is connected to c. Two of these two-way switches S1 and S2 are connected to a bulb as shown below.
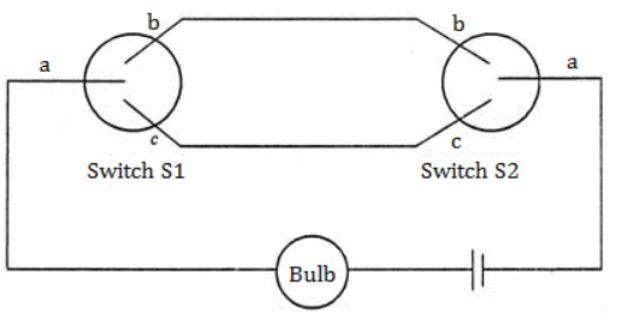
Which of the following expressions, if true, will always result in the lighting of the bulb ?
 | |
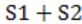 | |
 | |
 |

From this we can clearly know that given is EX-NOR operation i.e.,
(S1⊙S2) = (S1⊕S2)'
Question 11 |
How many pulses are needed to change the contents of a 8-bit up counter from 10101100 to 00100111 (rightmost bit is the LSB)?
134 | |
133 | |
124 | |
123 |
→ First counter is move from 172 to 255 = 83 pulses
→ 255 to 0 = 1 pulse
→ 0 to 39 = 39 pulses
Total = 83 + 1 + 39 = 123 pulses
Question 12 |
The numbers 1, 2, .... n are inserted in a binary search tree in some order. In the resulting tree, the right subtree of the root contains p nodes. The first number to be inserted in the tree must be
p | |
p + 1 | |
n - p | |
n - p + 1 |
RST contains elements = p
Root contains = 1 element
1st contains = n - (p + 1) element
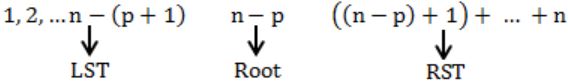
Root contains the value is n - p.
Question 13 |
A function f defined on stacks of integers satisfies the following properties.
f(∅) = 0 and f (push (S, i)) = max (f(S), 0) + i for all stacks S and integers i.
If a stack S contains the integers 2, -3, 2, -1, 2 in order from bottom to top, what is f(S)?
6 | |
4 | |
3 | |
2 |
f(Ø)=0 and f(push(S,i) = max(f(S),0) + i;
Initially stack is empty and for empty stack 0 is given.
f(push(0,2)) = max(f(Ø),0) + 2 = max(Ø,0) + 2 = 2
f(push(2,-3)) = max(2,0) + (-3) = 2 - 3 = -1
f(push(-1,2)) = max(-1,0) + 2 = 0 + 2 = 2
f(push(2,-1)) = max(2,0)+ (-1) = 2 - 1 = 1
f(push(1,2)) = max(1,0) + 2 = 1 + 2 = 3
So, 3 will be the answer.
∴ Option C is correct.
Question 14 |
In a depth-first traversal of a graph G with n vertices, k edges are marked as tree edges. The number of connected components in G is
k | |
k + 1 | |
n - k - 1 | |
n - k |
In this question, we are going to applying the depth first search traversal on each component of graph where G is connected (or) disconnected which gives minimum spanning tree
i.e., k = n-p
p = n - k
Question 15 |
In the following table, the left column contains the names of standard graph algorithms and the right column contains the time complexities of the algorithms. Match each algorithm with its time complexity.
1. Bellman-Ford algorithm A: O ( m log n) 2. Kruskal’s algorithm B: O (n3) 3. Floyd-Warshall algorithm C: O (nm) 4. Topological sorting D: O (n + m)
1→ C, 2 → A, 3 → B, 4 → D | |
1→ B, 2 → D, 3 → C, 4 → A | |
1→ C, 2 → D, 3 → A, 4 → B | |
1→ B, 2 → A, 3 → C, 4 → D |
Krushkal's algorithm → O(m log n)
Floyd-Warshall algorithm → O(n3)
Topological sorting → O(n+m)
Question 16 |
A hash table contains 10 buckets and uses linear probing to resolve collisions. The key values are integers and the hash function used is key % 10. If the values 43, 165, 62, 123, 142 are inserted in the table, in what location would the key value 142 be inserted?
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
6 |
165%10 = 5 [occupy 5]
62%10 = 2 [occupy 2]
123%10 = 3 [3 already occupied, so occupies 4]
142%10 = 2 [2, 3, 4, 5 are occupied, so it occupies 6]
Question 17 |
A student wishes to create symbolic links in a computer system running Unix. Three text files named "file 1", "file 2" and "file 3" exist in her current working directory, and the student has read and write permissions for all three files. Assume that file 1 contains information about her hobbies, file 2 contains information about her friends and file 3 contains information about her courses. The student executes the following sequence of commands from her current working directory
ln -s file 1 file 2 ln -s file 2 file 3
Which of the following types of information would be lost from her file system?
(I) Hobbies (II) Friends (III) Courses
(I) and (II) only | |
(II) and (III) only | |
(II) only | |
(I) and (III) only |
Question 18 |
The shell command
find -name passwd -print
is executed in /etc directory of a computer system running Unix. Which of the following shell commands will give the same information as the above command when executed in the same directory?
ls passwd | |
cat passwd | |
grep name passwd | |
grep print passwd |
Question 19 |
A user level process in Unix traps the signal sent on a Ctrl-C input, and has a signal handling routine that saves appropriate files before terminating the process. When a Ctrl-C input is given to this process, what is the mode in which the signal handling routine executes?
kernel mode | |
superuser mode | |
privileged mode | |
user mode |
Question 20 |
The Function Point (FP) calculated for a software project are often used to obtain an estimate of Lines of Code (LOC) required for that project. Which of the following statements is FALSE in this context.
The relationship between FP and LOC depends on the programming language used to implement the software. | |
LOC requirement for an assembly language implementation will be more for a given FP value, than LOC for implementation in COBOL | |
On an average, one LOC of C++ provides approximately 1.6 times the functionality of a single LOC of FORTRAN | |
FP and LOC are not related to each other |
Question 21 |
Consider the entities 'hotel room', and 'person' with a many to many relationship 'lodging' as shown below:

If we wish to store information about the rent payment to be made by person (s) occupying different hotel rooms, then this information should appear as an attribute of
Person | |
Hotel Room | |
Lodging | |
None of these. |
Question 22 |
A table has fields Fl, F2, F3, F4, F5 with the following functional dependencies
F1 → F3, F2→ F4, (F1.F2) → F5
In terms of Normalization, this table is in
1 NF | |
2 NF | |
3 NF | |
None |
F2 → F4 ......(ii)
(F1⋅F2) → F5 .....(iii)
F1F2 is the candidate key.
F1 and F2 are the prime key.
In (i) and (ii) we can observe that the relation from P → NP which is partial dependency. So this is in 1NF.
